what is happening with triangle badminton club
what is happening with triangle badminton club
In this article, nosotros are going to learn near the simplest form of a polygon, a triangle . All polygons tin exist divided into triangles, or in other words, they are formed by combining two or more triangles. Thus, agreement the basic properties of a triangle and its types is essential.
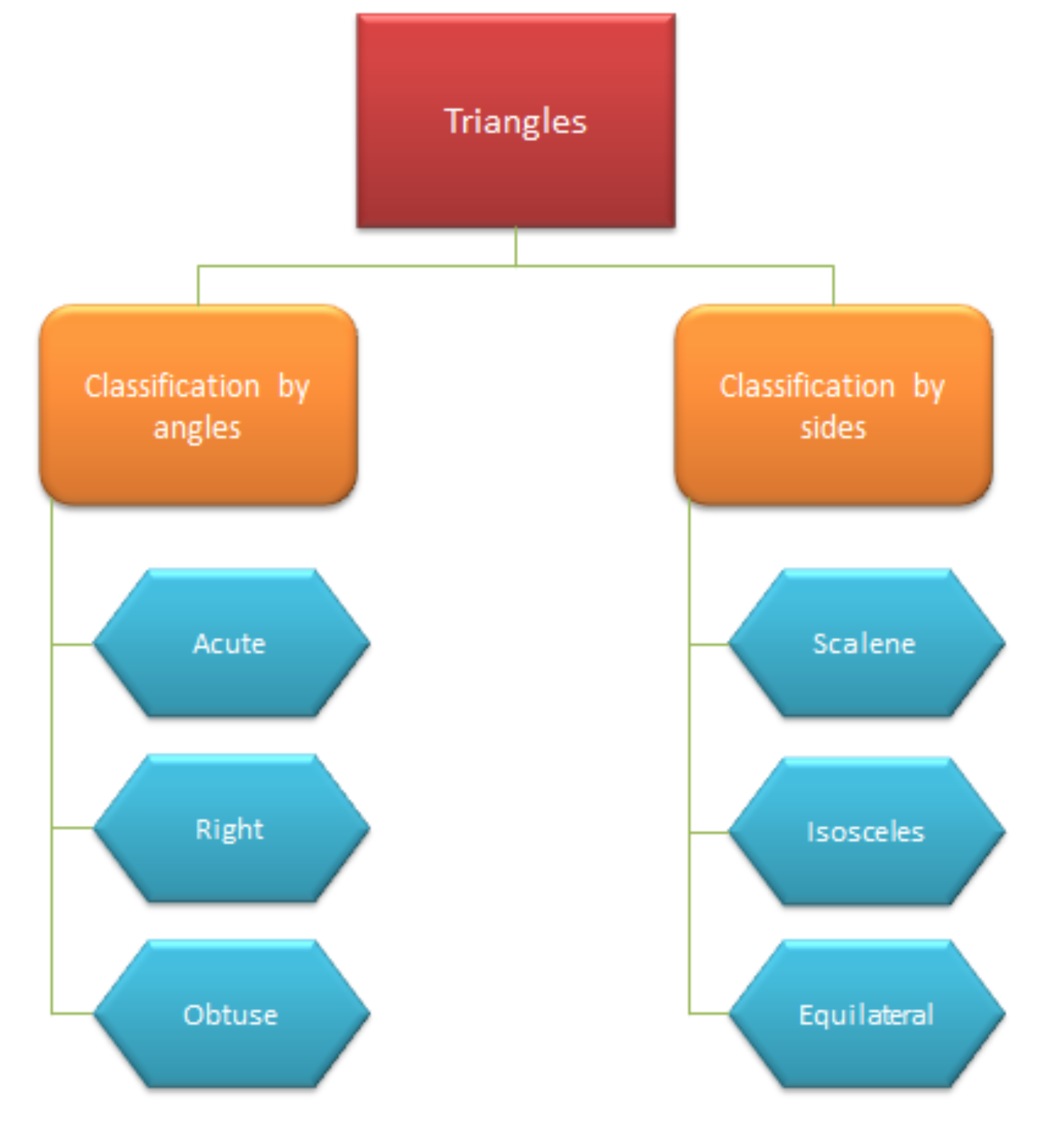
At that place are six types of triangles in total – Isosceles, Scalene, Equilaterial, Oblique, Acute, and Right. Based on the classification co-ordinate to internal angles, there are 3 types – Equilateral, Isosceles, and Scalene. Whereas, the types of a triangle that are classified according to the length of its side are Right, Acute, and Oblique. Hither are the types of triangles:
| Based on the Bending | Based on the Sides |
| Acute Angled Triangle | Equilateral Triangle |
| Oblique angled Triangle | Scalene Triangle |
| Right Bending Triangle | Isosceles Triangle |
Sentry this video to know the basic property of triangle:
Here is an outline of the topics we will cover in this article:
What is a triangle?
As the proper name suggests, the triangle is a polygon that has three angles. Then, when does a closed figure has three angles?
When it has 3 line segments joined end to end.
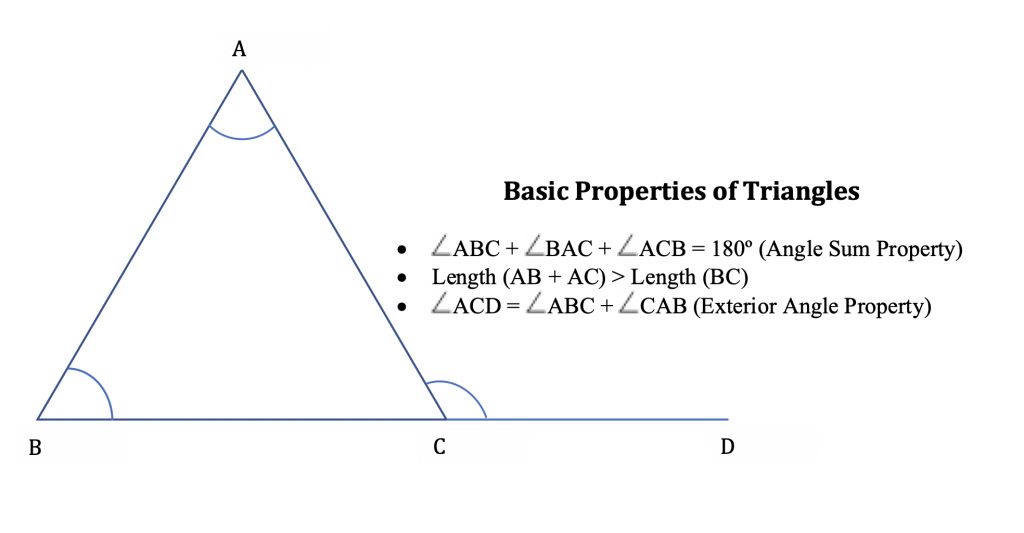
Thus, we can say that a triangle is a polygon, which has three sides, three angles, three vertices and the sum of all three angles of whatsoever triangle equals 180°.
Properties of a triangle
The backdrop of a triangle are:
- A triangle has three sides, three angles, and three vertices.
- The sum of all internal angles of a triangle is always equal to 180°. This is called the angle sum belongings of a triangle.
- The sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
- The side opposite to the largest angle of a triangle is the largest side.
- Any exterior angle of the triangle is equal to the sum of its interior reverse angles. This is called the exterior angle property of a triangle.
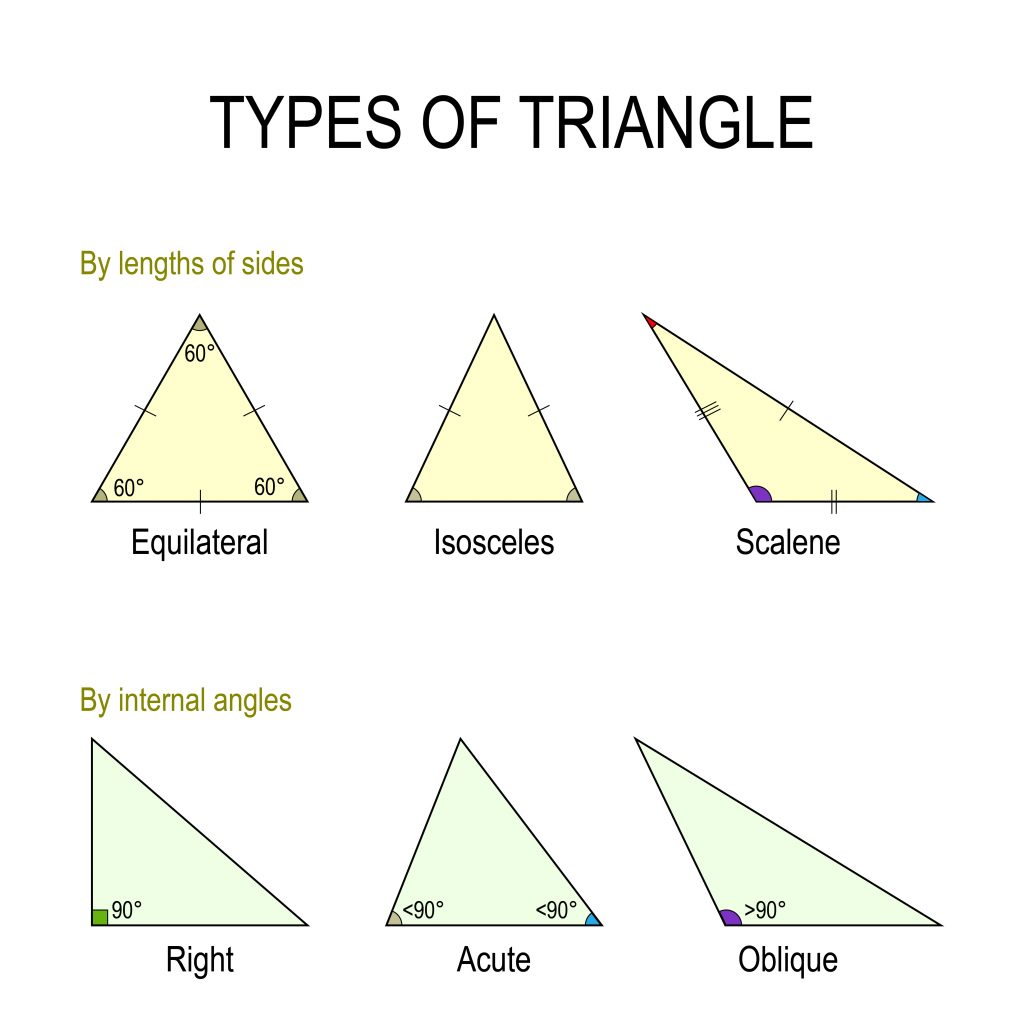
Types of triangles
Triangles can exist classified in 2 major ways:
- Classification co-ordinate to internal angles (Correct, Acute, Oblique)
- Classification according to the length of its sides (Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene)
Let's wait into the six types of triangles in detail:
- Acute Angled Triangle
- Right-Angled Triangle
- Oblique Angled Triangle
- Scalene Angled Triangle
- Isosceles Angled Triangle
- Equilateral Angled triangle
Astute Bending Triangle
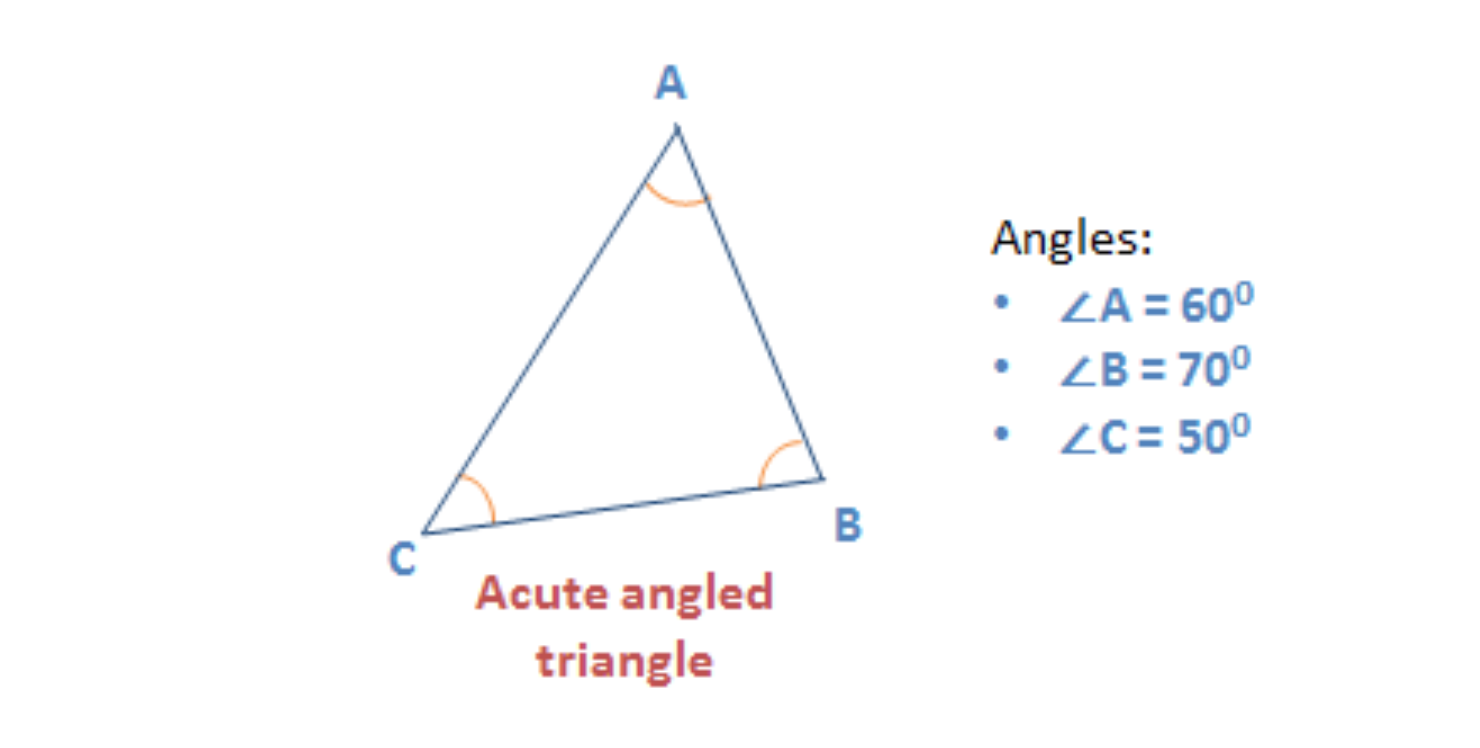
A triangle that has all three angles less than 90 ° is an acute angle triangle.
- So, all the angles of an astute angle triangle are called acute angles
Given below is an example of an astute angle triangle.
Right-Angle Triangle
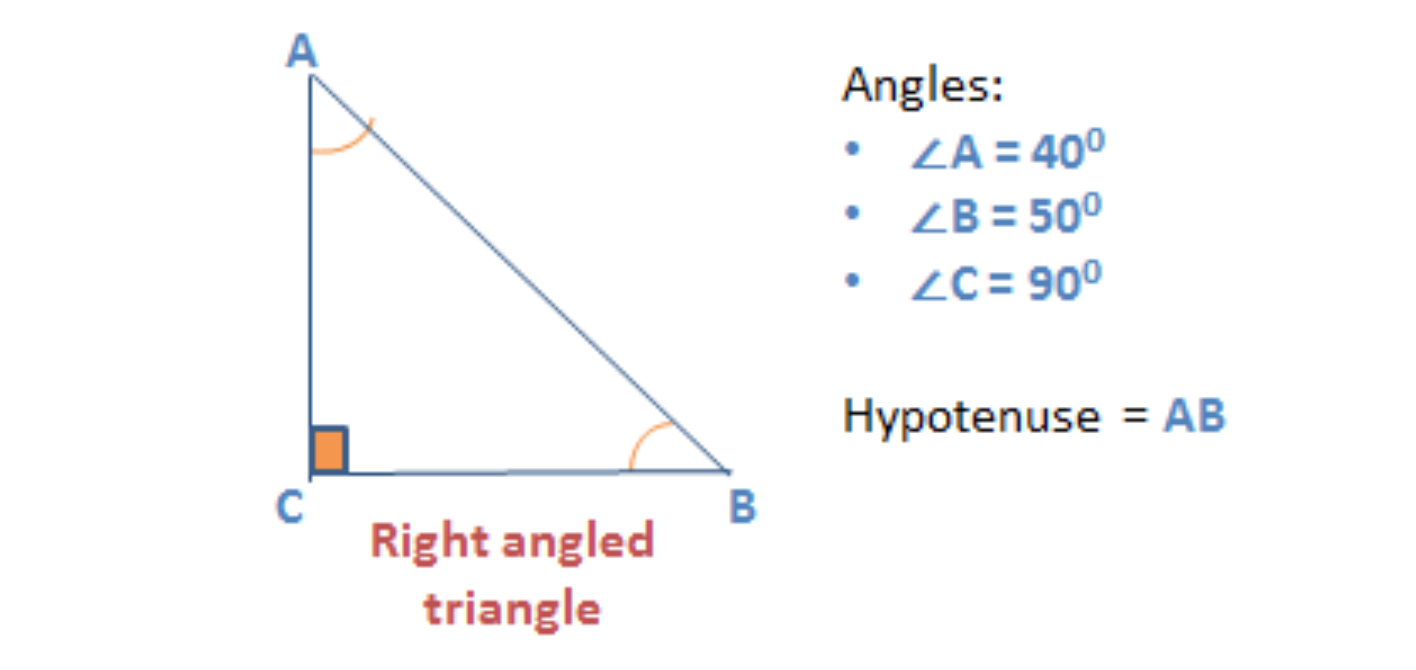
A triangle that has one angle that measures exactly 90 ° is a right-angle triangle.
- The other two angles of a right-bending triangle are acute angles.
- The side opposite to the right angle is the largest side of the triangle and is called the hypotenuse.
In a right-angled triangle, the sum of squares of the perpendicular sides is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
For e.k. because the higher up correct-angled triangle ACB, nosotros can say:
(AC)^2 + (CB)^2 = (AB)^2
This is known as Pythagoras theorem
Vice versa, nosotros can say that if a triangle satisfies the Pythagoras condition, then it is a right-angled triangle.
Obtuse/Oblique Angle Triangle
A triangle that has ane angle that measures more than than 90 ° is an obtuse angle triangle.
Given below is an example of an obtuse/oblique angle triangle.
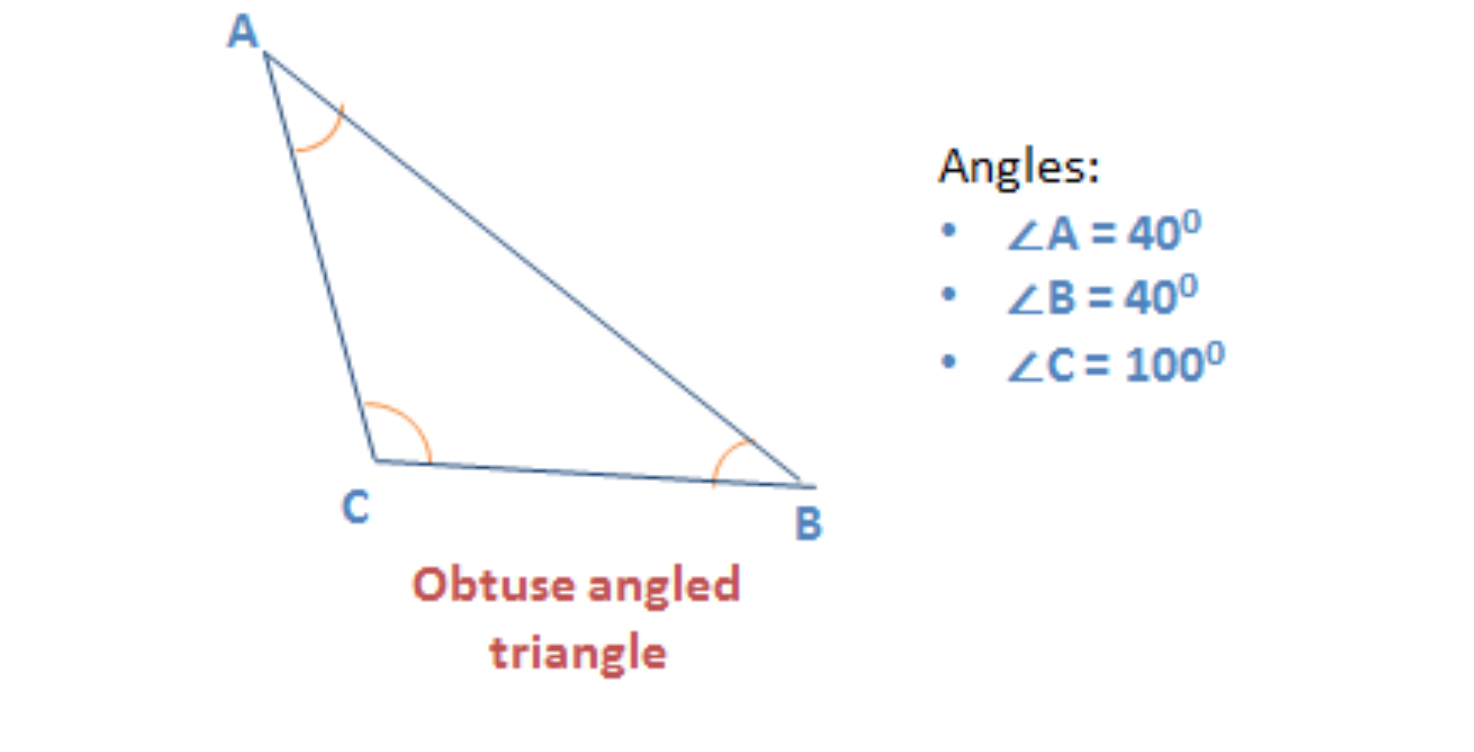
Questions on triangles are very commonly asked on the GMAT. Ace GMAT Quant by signing up for our free trial and get admission to 400+ questions. We are the most reviewed online GMAT Prep visitor with 2060+ reviews on GMATClub.
Salve 60+ hours of GMAT preparation by crafting a well-defined study program in just 3 steps:
Scalene triangle
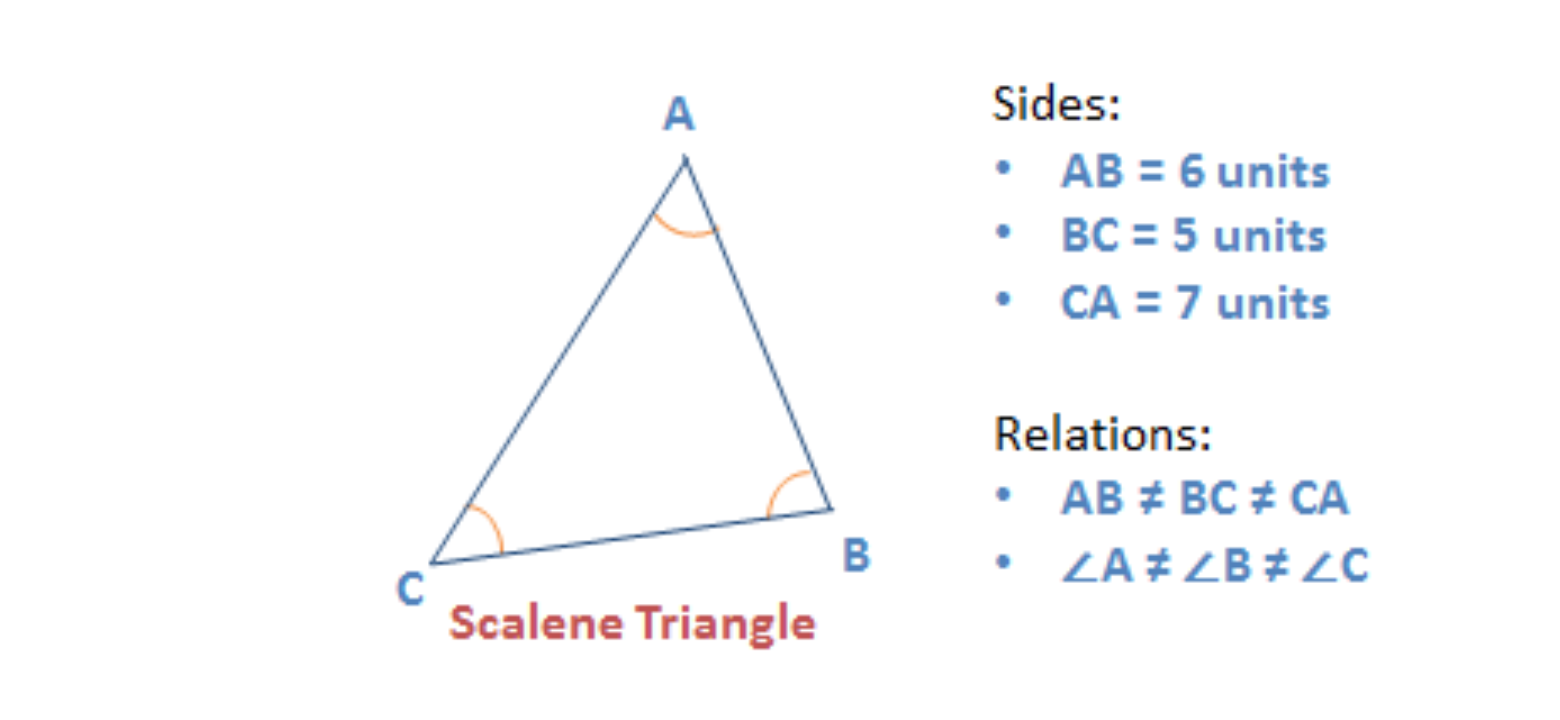
A triangle that has all 3 sides of different lengths is a scalene triangle.
- Since all the three sides are of different lengths, the three angles will also exist unlike.
Given beneath is an example of a scalene triangle
Isosceles triangle
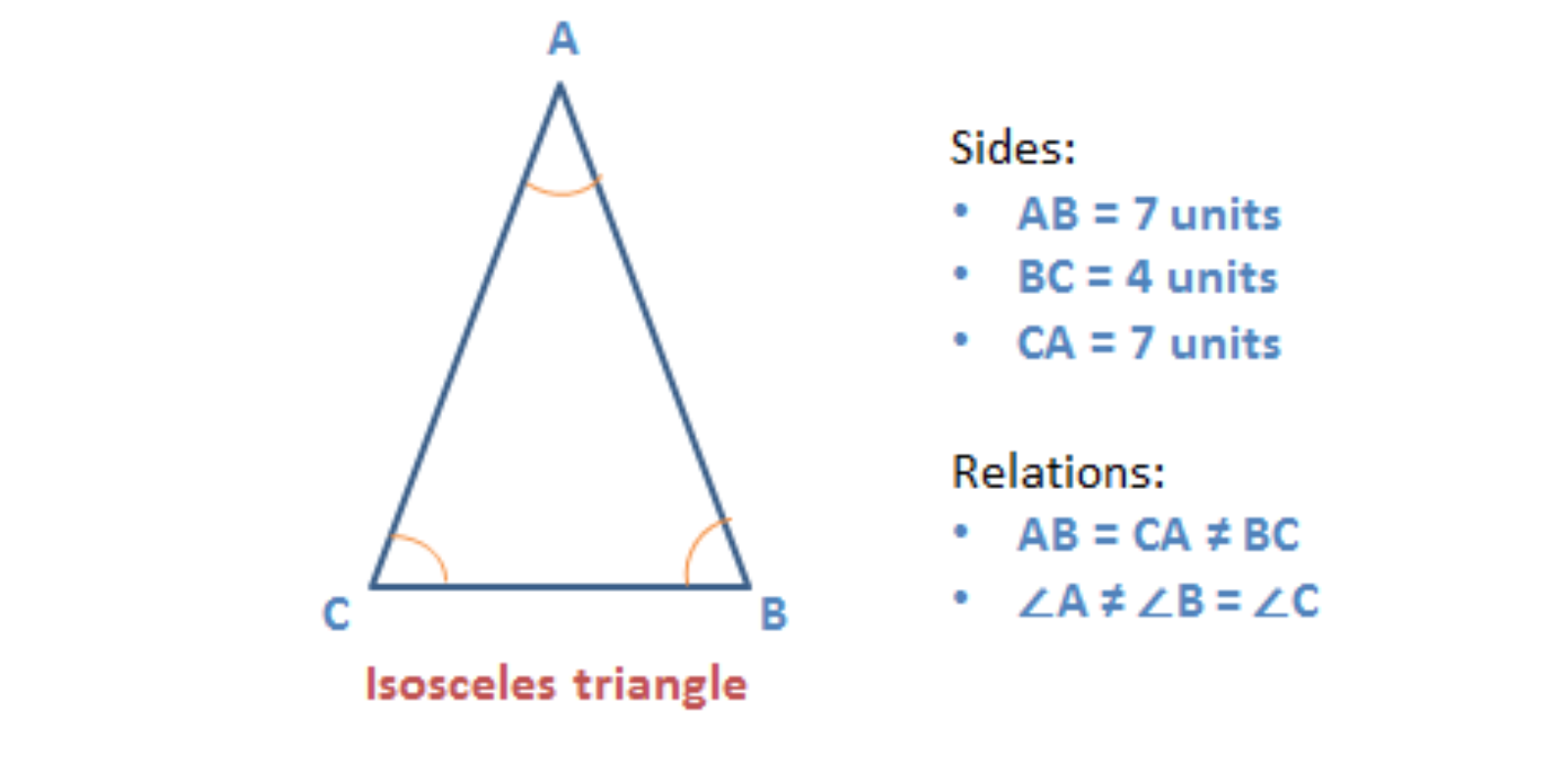
A triangle that has two sides of the same length and the third side of a dissimilar length is an isosceles triangle.
- The angles opposite the equal sides measure the aforementioned.
Given below is an instance of an isosceles triangle.
Equilateral triangle
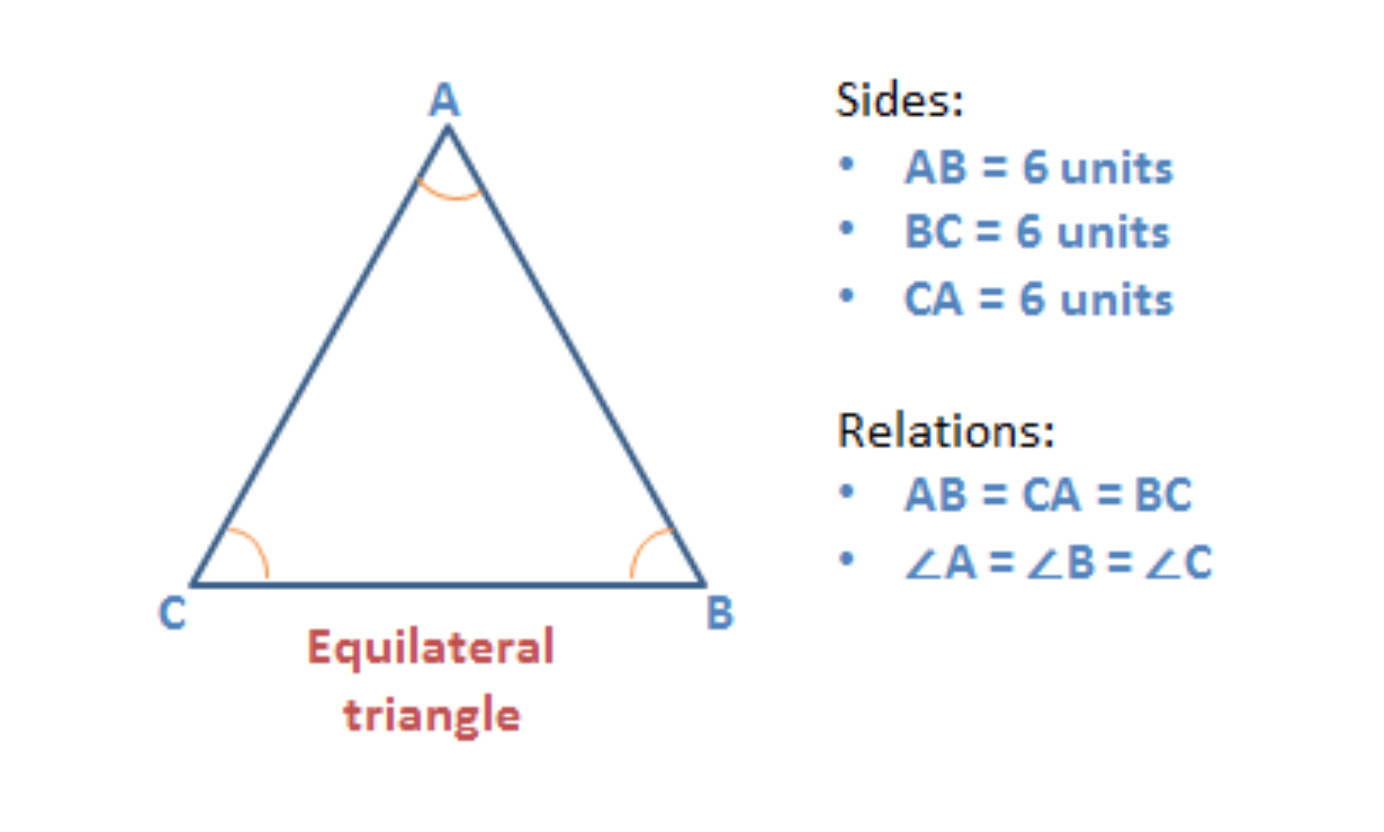
A triangle that has all three sides of the same length is an equilateral triangle.
- Since all the iii sides are of the same length, all the three angles will also be equal.
- Each interior angle of an equilateral triangle = threescore°
Special cases of Correct Angle Triangles
Let's besides see a few special cases of a right-angled triangle
45-45-90 triangle
In this triangle,
- Two angles measure out 45°, and the 3rd angle is a right angle.
- The sides of this triangle will exist in the ratio – 1: 1: √two respectively.
- This is also called an isosceles right-angled triangle since two angles are equal.
30-lx-90 triangle
In this triangle,
- This is a right-angled triangle, since ane angle = 90°
- The angles of this triangle are in the ratio – ane: two: 3, and
- The sides reverse to these angles will be in the ratio – i: √3: two respectively
- This is a scalene right-angled triangle since all 3 angles are different.
Area of Triangle
- Area of any triangle = ½ * base * meridian
- Area of a right-angled triangle = ½ * product of the ii perpendicular sides
Backdrop of Triangle: Summary & Key Takeaways
Let us summarize some of the important properties of a triangle.
- The sum of all interior angles of any triangle is equal to 180 °
- The sum of all exterior angles of whatever triangle is equal to 360 °
- An exterior bending of a triangle is equal to the sum of its two interior opposite angles
- The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the tertiary side
- Similarly, the deviation between the lengths of whatsoever ii sides of a triangle is always less than the length of the third side
- The side opposite to the smallest interior angle is the shortest side and vice versa.
- Similarly, the side opposite to the largest interior angle is the longest side and vice versa.
- In the instance of a right-angled triangle, this side is called the hypotenuse
- The elevation of a triangle is equal to the length of the perpendicular dropped from a vertex to its opposite side, and this side is considered the base of operations
If you liked this article, yous may likewise similar to read the following advanced level articles on triangles
- GMAT Geometry Concepts and Formulas on Triangles (Part-ane)
- Backdrop of Triangles: Practice Questions (Role-2)
- Special Properties of Triangles (Part-3)
Starting with your GMAT training? Hither is a five step preparation program to ace the GMAT:
Properties of Triangle: Practice Question
Question: ane
In an isosceles triangle DEF, if an interior angle ∠D = 100° so what is the value of ∠F?
- 20°
- xl°
- lx°
- 80°
- 100°
Solution
Stride 1: Given
- ∆DEF is an isosceles triangle
- ∠D = 100°
Step 2: To find
- The value of ∠F
Step 3: Arroyo and Working out
- We know that the sum of all interior angles in a triangle = 180°
- Implies, ∠D + ∠E + ∠F = 180°
- ∠Due east + ∠F = 1800 – 1000 = 80°
- Since ∆DEF is an isosceles triangle; two of its angles must be equal.
- And the simply possibility is ∠Due east = ∠F
- Therefore, 2∠F = lxxx°
- Implies, ∠F = twoscore°
Hence the correct reply is Pick B.
Question 2
In a correct-angled triangle, ∆ABC, BC = 26 units and AB = 10 units. If BC is the longest side of the triangle, and so what is the expanse of ∆ABC?
- 120
- 130
- 240
- 260
- 312
Solution
Step 1: Given
- ∆ABC is a right-angled triangle
- BC = 26 units
- AB = 10 units
- BC is the longest side of the triangle
Pace 2: To observe
- The area of triangle ∆ABC
Stride 3: Arroyo and Working out
- We are given that BC is the longest side of the triangle, which implies that BC is the hypotenuse
Thus, co-ordinate to Pythagoras rule:
- BC2 = AB2 + AC2
- 262 = 10two + Air-conditioning2
- Air-conditioning2 = 676 – 100 = 576
- Therefore, Ac = 24 units
- We know that the area of a correct-angled triangle = ½ * product of the two perpendicular sides = ½ * AB * AC = ½ * x * 24 = 120 sq. units
Hence the correct respond is Choice A.
Hither are a few more articles that you may like to read:
- Properties of Quadrilateral
- Properties of Numbers: Even/Odd, Prime, and HCF & LCM
- Properties of Circle
- Properties of Lines and Angles
Questions on triangles are very unremarkably asked on the GMAT. Ace GMAT Quant by signing up for our free trial and become admission to 400+ questions. We are the most reviewed online GMAT Prep company with 2060+ reviews on GMATClub.
Did y'all know east-GMATers have reported more 700+ scores than e'er earlier in GMAT Society's history? Watch this video to empathise how e-GMAT has achieved this tape-shattering result past investing and innovating with a single goal in mind – To create a platform that empowers students to achieve and evangelize their very best.
FAQ – Properties of a triangle
What is a triangle and its properties?
A triangle is a airtight figure with three sides, 3 vertices, three angles, and the sum of internal angles is 180°
What are the different types of triangles?
Triangles tin be classified in ii ways, according to internal angles and according to the length of the sides. According to internal angles, there are three types of triangles i.e., acute, right, and obtuse-angled triangle. Co-ordinate to the length of sides, triangles can be classified into 3 categories i.due east., Scalene, Isosceles, and Equilateral triangle.
What is a Scalene triangle?
A triangle that has all three sides of different lengths is a scalene triangle.
What is an Isosceles triangle?
A triangle that has two sides of the same length and the third side of a different length is an isosceles triangle.
What is an equilateral triangle?
A triangle that has all three sides of the aforementioned length is an equilateral triangle.
what is happening with triangle badminton club
Posted by: valleyfoodursh.blogspot.com
0 Response to "what is happening with triangle badminton club"
Post a Comment